 |
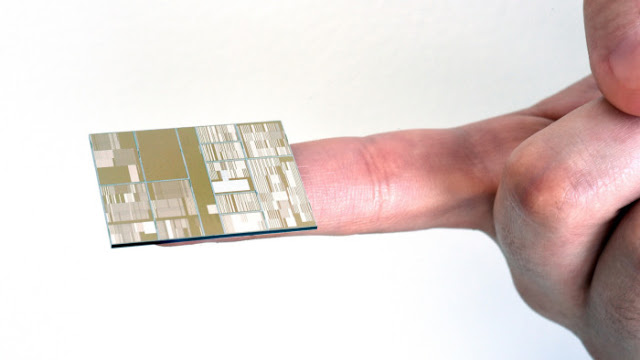
| IBM Nano Chip |
IBM has been working on this project since last year when it invested $3 billion in partnership with the state of New York, Samsung and the other technology suppliers for the purpose of chip research and design. IBM showed its prototype chip which is being seen as the potential breakthrough for the tiny transistors. A transistor is a tiny switch that is placed inside a computer and it helps it to power up. The Nano chips are so small and thin that they are 1/10,000th of the width of a human hair. These chips are a direct result of the research of IBM combined with the State University of New York Polytechnic Institute in Albany. Once these chips are incorporated in computers, it could allow about 20 billion transistors to be place on a chip of the size of a fingernail.
This study is also being considered to hold good with the Moore’s Law in Computing. Moore’s law states that the number of transistors per square inch on integrated circuits gets doubled every year.
Gordon Moore, a co-founder of Intel predicted these trends in 1965 and it would be right to say that it is still alive and applicable. Patrick Moorhead, who is an analyst at Moor Insights & Strategies said ,” This is research that has been done and is not an actual product, but it is a great example that Moore’s Law continues and shows the potential for smartphones, tablets, PCs and even cars to be twice as smart as they were before at the same energy level.”
However, in 2013 it was predicted by former Intel engineer, Robert Colwell that the Moore’s Law would be dead in the coming decade as shrinking the transistors beyond 7 or 5nm is extremely difficult. Today the normal chips are fabbed using the process technologies at scales of 22nm or 14nm. Shrinking these transistors affects them in terms of power consumption of the transistor. When shrinked, the dynamic power of the transistor drops, but the static consumption increases as they leak more current. With the right techniques these issues can be overcome.
These chips have been hailed as revolutionary but it will still take some time before they are widely available in the market.